In the dynamic world of financial markets, the ability to protect capital, maintain operational stability, and manage exposure is no longer optional. A robust trading risk management system is the backbone of any disciplined trading strategy, enabling organizations and individual traders alike to proactively identify, assess, and mitigate threats before they impact portfolios or business outcomes.

Effective risk management transforms uncertainty into calculated opportunity. It empowers organizations to build resilience against market volatility, regulatory changes, technological disruption, and unforeseen crisis scenarios. About the Microsoft dynamics GP partners with this strategic emphasis aligns with industry leading practices in broader risk management services and complements comprehensive business risk frameworks such as those provided by professional consultancies.

A trading risk management system is a structured, systematic set of processes, tools, and governance protocols designed to:
At its core, the system blends quantitative controls (such as position limits, stress testing, and scenario analysis) with qualitative oversight (governance, policy adherence, oversight committees). The goal is simple yet profound: protect capital while enabling growth within risk tolerances.

A trading risk management system is a structured, systematic set of processes, tools, and governance protocols designed to:

Early detection of potential threats is the starting point. This includes monitoring market price fluctuations, counterparty credit risk, and strategic misalignments within portfolios. Continuous surveillance ensures that emerging risks are visible across all levels of the organization.
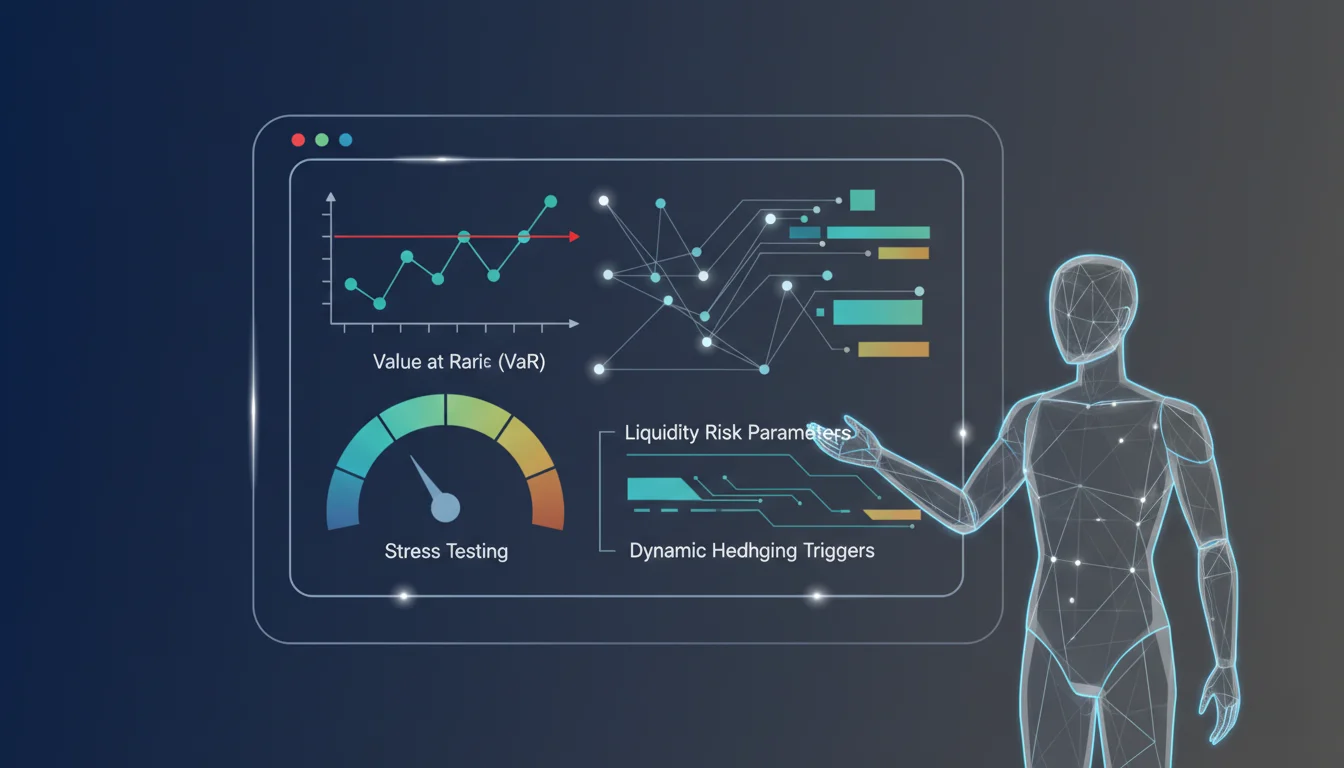

Robust statistical models and real-time risk engines establish limits on leverage, position sizes, and market exposures. Controls can include:
These controls effectively shape how trading strategies adapt to changing market conditions without exposing the organization to outsized risk.
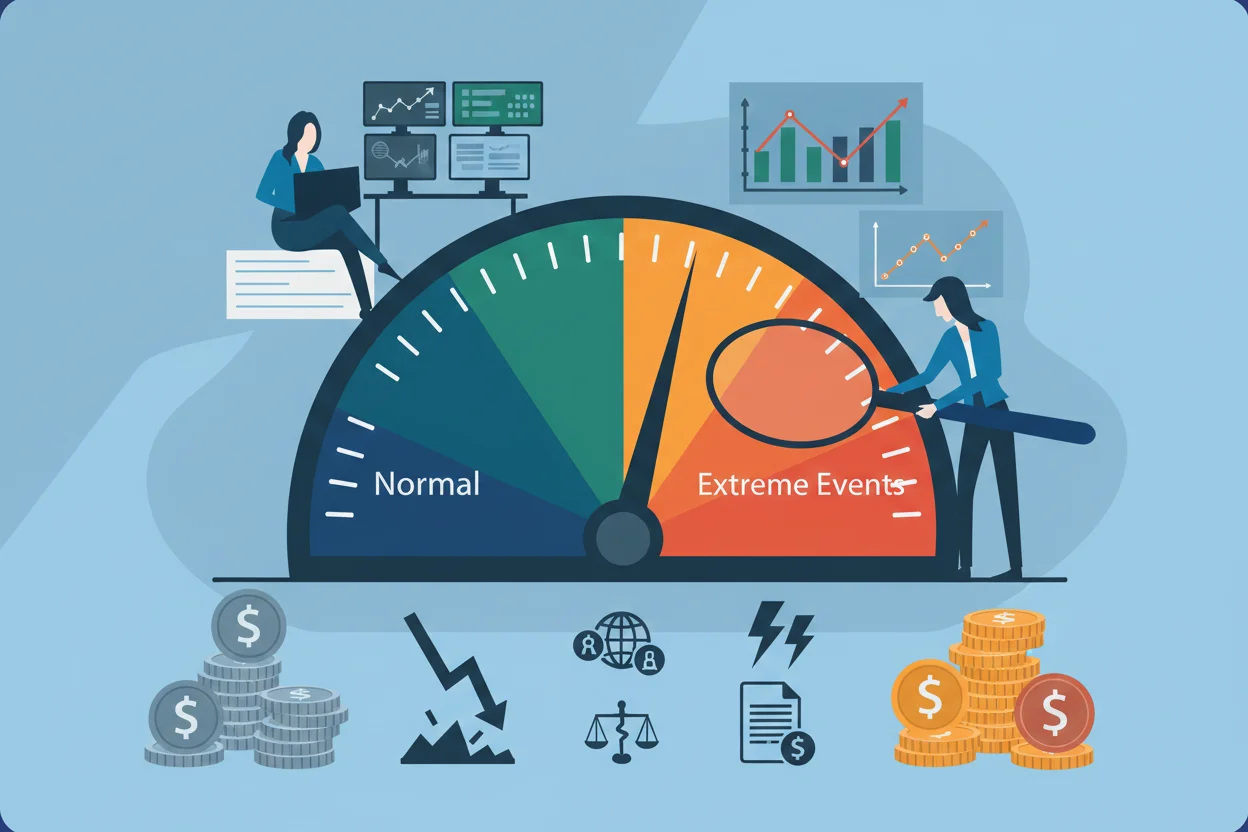

Markets don’t behave linearly. Scenario planning simulates extreme market events—such as flash crashes, geopolitical crises, or sudden regulatory changes—to assess system resilience. Stress testing offers insights into how portfolios might perform under adverse conditions and informs contingency planning.
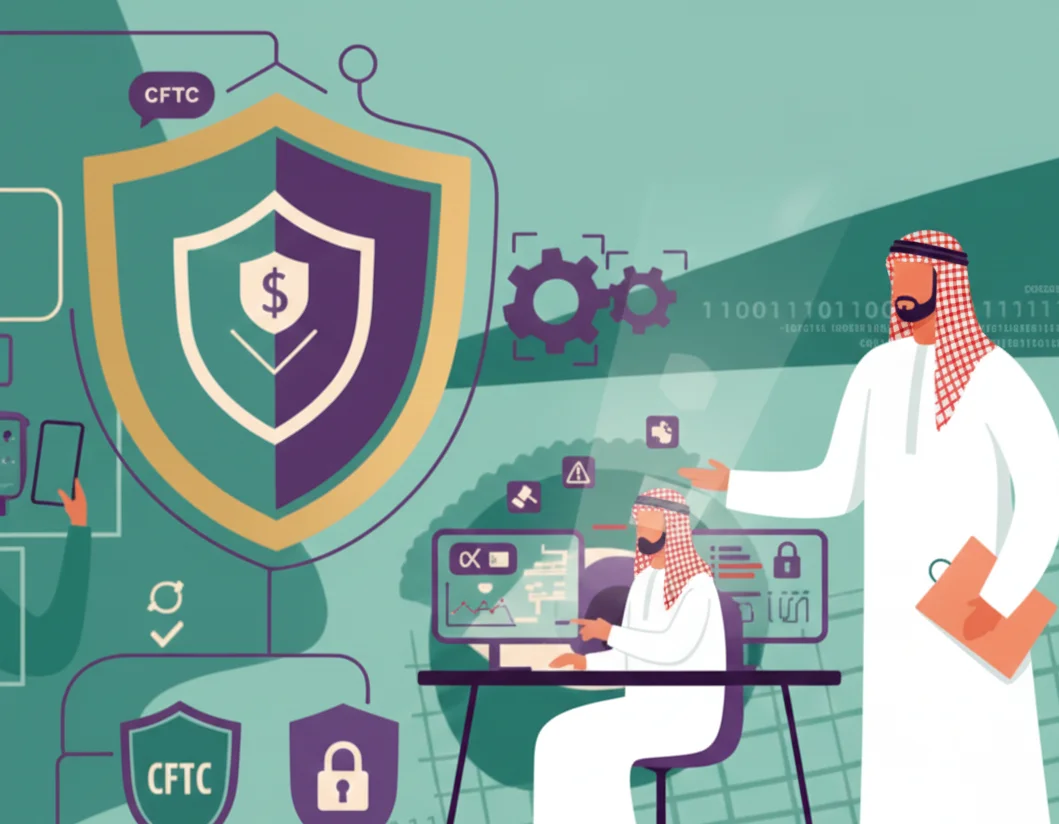

A governance framework defines who is accountable for risk decisions, how risk policies are reviewed, and how compliance is enforced. Compliance with evolving regulations (such as SEC and CFTC standards in the United States) is critical to maintaining operational legitimacy and reputational integrity.
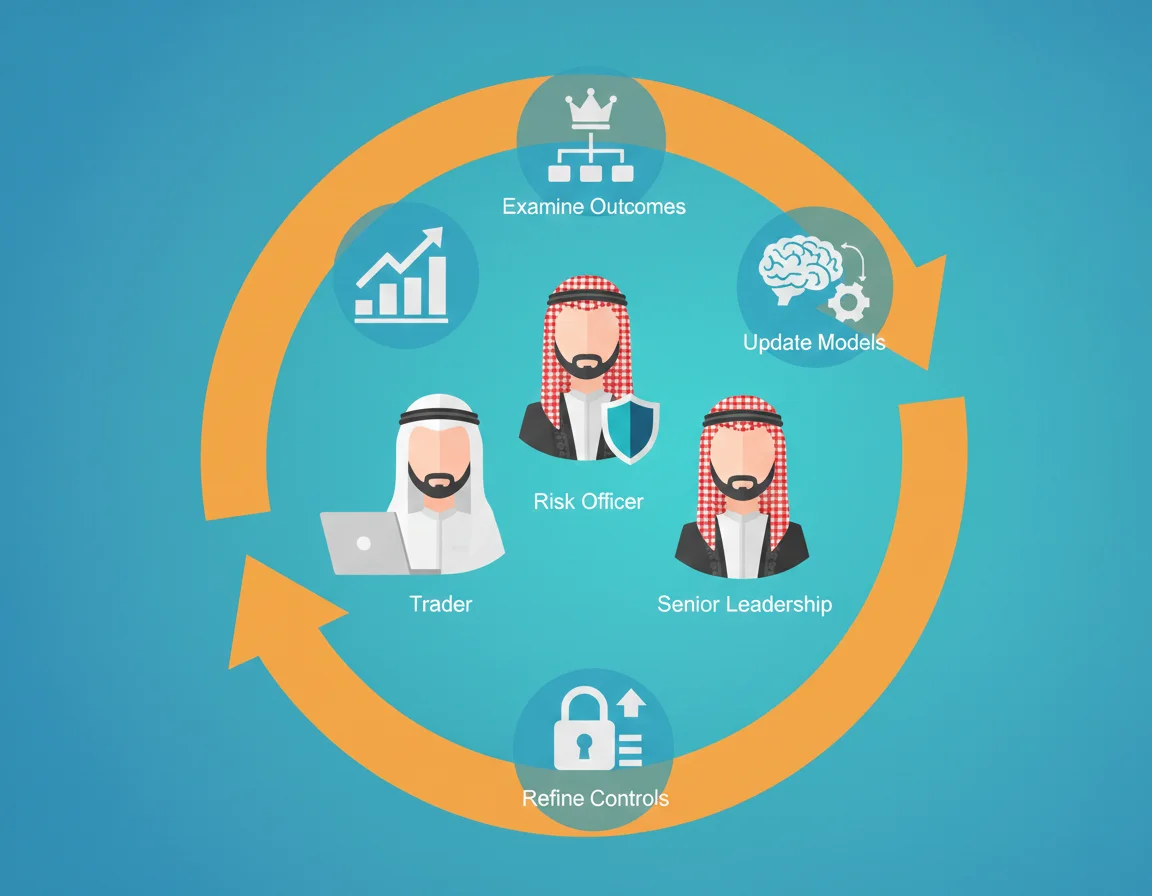
A feedback loop where traders, risk officers, and senior leadership examine outcomes, update models, and refine controls is essential for any sustainable trading risk management system.
Today’s markets are characterized by speed, complexity, and interconnected risk vectors. An isolated shock in one asset class can ripple across entire portfolios and institutions within seconds. Without a cohesive risk management strategy, firms expose themselves to:
A structured risk framework doesn’t eliminate risk; it manages it intelligently. In doing so, organizations can pursue innovation and expansion with confidence.

Professional risk consultancies emphasize proactive over reactive risk management. Firms that lead in this space stress the importance of identifying threats before they materialize, assessing impacts holistically, and embedding risk culture throughout the organization. Tailored services in broader risk management services often include strategic threat assessments, supply chain risk analysis, travel risk protocols, business continuity planning, and crisis response frameworks.
The same principles that apply to physical and strategic risk in a corporate context—such as those used by expert risk advisers—can be adapted to trading environments:
Understand inherent weaknesses in your trading architecture.
Prepare for market shocks and systemic events.
Track exposures in real time and adjust controls based on active intelligence.
Modern trading risk management systems leverage advanced technology stacks. These include:
When appropriately implemented, these tools not only reduce human error but also ensure risk controls operate at the speed of the markets they govern. Advanced automation helps firms transition from manual review cycles to continuous risk enforcement.

While technology accelerates risk functions, human insight remains indispensable. Skilled risk managers interpret data, stress test assumptions, and make judgement calls that algorithms cannot. Building a culture where risk awareness permeates every decision—especially in high stakes trading environments—is a competitive differentiator.
Just as organizations benefit from external strategic partners for areas such as SharePoint intranet development services and cloud application modernization, successful trading teams integrate diverse expertise to optimize operations and manage risk holistically.
Organizations can strengthen their risk posture by integrating their trading risk frameworks with broader operational tools and services that enhance efficiency and governance:
These integrations improve data visibility and operational controls—both of which are key inputs to any scalable risk management system.




What is a safety risk management system?
A safety risk management system is a structured approach to identifying, analyzing, controlling, and monitoring hazards that could lead to harmful events. It integrates policies, procedures, technology, and accountability to protect people, assets, and operations in both trading and organizational environments.
How does risk management differ from safety risk management?
Risk management broadly addresses financial, strategic, operational, and compliance risks. Safety risk management specifically focuses on preventing physical or operational harm—such as workplace safety, systems failures, or injury—through hazard controls, training, and monitoring systems.
Why is safety risk management essential for trading operations?
While trading is a financial activity, the systems, infrastructure, and human factors involved carry operational risks. Safety risk management ensures that technology platforms remain secure, that workflow processes are resilient, and that any physical or systemic risks to personnel or systems are mitigated.
How do you implement an effective safety risk management framework?
Start with hazard identification, proceed with risk assessment, establish control measures, document procedures, and implement continuous monitoring. Training and leadership ownership are vital to sustain adoption and effectiveness.
What tools support safety risk management systems?
Tools include incident reporting platforms, real-time monitoring dashboards, compliance tracking software, and integrated governance systems that align risk indicators with actionable controls.
What role does regulatory compliance play in safety risk management?
Regulatory compliance provides mandatory controls, reporting standards, and safety benchmarks. Compliance ensures operations are legally defensible and aligned with industry best practices, reducing liabilities and enhancing trust.
Can safety risk management improve business performance?
By preventing incidents, reducing downtime, enhancing worker confidence, and promoting resilient processes, safety risk management drives operational continuity and market credibility.